GWT Junit集成
GWT Junit集成 示例
以下将是eclipse中的项目结构。
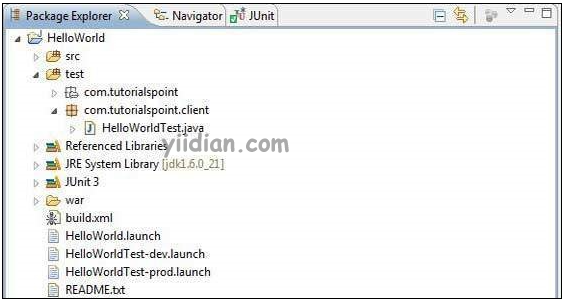
以下是修改后的模块描述符src/com.yiidian/HelloWorld.gwt.xml 的内容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<module rename-to = 'helloworld'>
<!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. -->
<inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/>
<!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. -->
<inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/>
<!-- Inherit the UiBinder module. -->
<inherits name = "com.google.gwt.uibinder.UiBinder"/>
<!-- Specify the app entry point class. -->
<entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/>
<!-- Specify the paths for translatable code -->
<source path = 'client'/>
<source path = 'shared'/>
</module>
以下是修改后的样式表文件war/HelloWorld.css 的内容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改后的 HTML 主机文件war/HelloWorld.html 的内容。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JUnit Integration Demonstration</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
将src/com.yiidian/client包中的 HelloWorld.java 内容替换为以下内容
package com.yiidian.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.GWT;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickHandler;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyCodes;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyUpEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyUpHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.Window;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Button;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.DecoratorPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HasHorizontalAlignment;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HorizontalPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Label;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TextBox;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.VerticalPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
public void onModuleLoad() {
/*create UI */
final TextBox txtName = new TextBox();
txtName.setWidth("200");
txtName.addKeyUpHandler(new KeyUpHandler() {
@Override
public void onKeyUp(KeyUpEvent event) {
if(event.getNativeKeyCode() == KeyCodes.KEY_ENTER){
Window.alert(getGreeting(txtName.getValue()));
}
}
});
Label lblName = new Label("Enter your name: ");
Button buttonMessage = new Button("Click Me!");
buttonMessage.addClickHandler(new ClickHandler() {
@Override
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
Window.alert(getGreeting(txtName.getValue()));
}
});
HorizontalPanel hPanel = new HorizontalPanel();
hPanel.add(lblName);
hPanel.add(txtName);
hPanel.setCellWidth(lblName, "130");
VerticalPanel vPanel = new VerticalPanel();
vPanel.setSpacing(10);
vPanel.add(hPanel);
vPanel.add(buttonMessage);
vPanel.setCellHorizontalAlignment(buttonMessage,
HasHorizontalAlignment.ALIGN_RIGHT);
DecoratorPanel panel = new DecoratorPanel();
panel.add(vPanel);
// Add widgets to the root panel.
RootPanel.get("gwtContainer").add(panel);
}
public String getGreeting(String name){
return "Hello "+name+"!";
}
}
将test/com.yiidian/client包中的 HelloWorldTest.java 内容替换为以下内容
package com.yiidian.client;
import com.tutorialspoint.shared.FieldVerifier;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.GWT;
import com.google.gwt.junit.client.GWTTestCase;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.ServiceDefTarget;
/**
* GWT JUnit tests must extend GWTTestCase.
*/
public class HelloWorldTest extends GWTTestCase {
/**
* must refer to a valid module that sources this class.
*/
public String getModuleName() {
return "com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorldJUnit";
}
/**
* tests the FieldVerifier.
*/
public void testFieldVerifier() {
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName(null));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName(""));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName("a"));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName("ab"));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName("abc"));
assertTrue(FieldVerifier.isValidName("abcd"));
}
/**
* this test will send a request to the server using the greetServer
* method in GreetingService and verify the response.
*/
public void testGreetingService() {
/* create the service that we will test. */
GreetingServiceAsync greetingService =
GWT.create(GreetingService.class);
ServiceDefTarget target = (ServiceDefTarget) greetingService;
target.setServiceEntryPoint(GWT.getModuleBaseURL()
+ "helloworld/greet");
/* since RPC calls are asynchronous, we will need to wait
for a response after this test method returns. This line
tells the test runner to wait up to 10 seconds
before timing out. */
delayTestFinish(10000);
/* send a request to the server. */
greetingService.greetServer("GWT User",
new AsyncCallback<String>() {
public void onFailure(Throwable caught) {
/* The request resulted in an unexpected error. */
fail("Request failure: " + caught.getMessage());
}
public void onSuccess(String result) {
/* verify that the response is correct. */
assertTrue(result.startsWith("Hello, GWT User!"));
/* now that we have received a response, we need to
tell the test runner that the test is complete.
You must call finishTest() after an asynchronous test
finishes successfully, or the test will time out.*/
finishTest();
}
});
/**
* tests the getGreeting method.
*/
public void testGetGreeting() {
HelloWorld helloWorld = new HelloWorld();
String name = "Robert";
String expectedGreeting = "Hello "+name+"!";
assertEquals(expectedGreeting,helloWorld.getGreeting(name));
}
}
}
使用生成的启动配置在 Eclipse 中运行测试用例
我们将使用 webAppCreator 为开发模式和生产模式生成的启动配置在 Eclipse 中运行单元测试。
在开发模式下运行 JUnit 测试
- 从 Eclipse 菜单栏中,选择运行 → 运行配置...
- 在 JUnit 部分下,选择 HelloWorldTest-dev
- 要保存对参数的更改,请按应用
- 要运行测试,请按运行
如果您的应用程序一切正常,这将产生以下结果 -
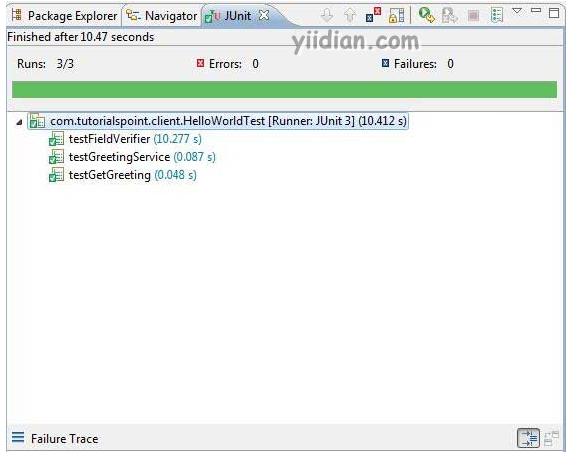
在生产模式下运行 JUnit 测试
- 从 Eclipse 菜单栏中,选择运行 → 运行配置...
- 在 JUnit 部分下,选择 HelloWorldTest-prod
- 要保存对参数的更改,请按应用
- 要运行测试,请按运行
如果您的应用程序一切正常,这将产生以下结果 -

热门文章
优秀文章


