

我想在R^n中生成一个随机定向的圆。我已经能够成功地在n球体的表面上生成点。我读到你可以将它与平面相交并得到一个圆,但我不知道在Python中如何做到这一点。
或者有没有其他方法可以在Python中生成它?
谢谢!
由于您已经知道如何在n球体的表面上生成一个随机点,因此只需生成两个这样的点,将它们称为P1和P2。这些将决定圆所在的平面。
我假设这两个点与原点的距离都是1(如果你选择1作为n球的半径,这将是正确的)。如果不是,请将每个点除以它的长度。
现在我们想让P2垂直于P1。这可以通过
P2 = P2 - dot(P1, P2) P1
P2 = P2 / || P2 ||
然后对于每个点,您可以生成一个0到2pi之间的随机角度。通过以下方式将此角度转换为圆上的点:
cos(angle) * P1 + sin(angle) * P2.
您需要为此使用2个基向量。
>
生成随机单元N-D向量U
所以只需创建N个随机数的数组用户界面=
生成垂直于U的N-D向量V
在2D和3D是这么简单,你可以交换x,y并在2D中否定一个,或者在3D中使用向量积。不幸的是,向量积在N-D中没有定义(至少据我所知没有),所以你需要生成点积为零的非零向量:
(U.V) = dot(U,V) = 0
u0.v0 + u1.v1 . u2.v2 + ... = 0
因此,您可以创建一些随机元素并适合其余元素(因此总和为零)。为了均衡,您可以使用abs高vi,其中用户界面的abs低…在此之后,将V规范化为单位大小。
在下面的C示例中,我使用了这种方法:
v[i]=还要注意V不能为零!!!
N-D中的圆
使用简单的参数方程:
P(t) = center + radius*cos(t)*U + radius*sin(t)*V
其中t=
这里生成U, V的简单C示例:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
const int n=5; // dimension count
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
double nd_dot(double *a,double *b) // = (a.b)
{
int i; double c;
for (c=0.0,i=0;i<n;i++) c+=a[i]*b[i];
return c;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void nd_unit(double *a) // a = a / |a|
{
int i; double c;
for (c=0.0,i=0;i<n;i++) c+=a[i]*a[i];
c=sqrt(c); if (c>1e-10) c=1.0/c; else c=0.0;
for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]*=c;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
double nd_length(double *a) // = |a|
{
int i; double c;
for (c=0.0,i=0;i<n;i++) c+=a[i]*a[i];
return sqrt(c);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void nd_rnd(double *a) // a = (? ? ? ... ?) , |a| = 1.0
{
int i; double c;
for (;;)
{
for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]=Random()-0.5;
for (c=0.0,i=0;i<n;i++) c+=a[i]*a[i];
if (c>1e-20) break;
}
c=1.0/sqrt(c);
for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]*=c;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void nd_perpendicular(double *a,double *b) // a = (? ? ? ... ?) , |a| = 1.0 , (a.b) = 0.0
{
if (n==1) // 1D case
{
if (fabs(b[0]>1e-10)) a[0]=1.0; else a[0]=1.0;
return;
}
int i; double c1,s;
for (c1=0.0,i=0;i<n;i++) // c1 = dot(a,b)
{
s=1.0; // s = signum of a[i] so (a.b) -> 0
if (b[i]<0.0) s=-1.0;
if (c1*s>0.0) s=-s;
a[i]=s*Random();
c1+=a[i]*b[i];
}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) // correct single element so (a.b) = 0
if (fabs(b[i])>1e-10)
{
c1-=a[i]*b[i];
a[i]=-c1/b[i];
break;
}
nd_unit(a);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AnsiString nd_prn(double *a) // this is for printing you can ignore this
{
int i; AnsiString s="( ";
for (i=0;i<n;i++) s+=AnsiString().sprintf("%6.3lf ",a[i]);
s+=" )"; return s;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// This is usage example in VCL you can ignore this:
__fastcall TForm1::TForm1(TComponent* Owner):TForm(Owner)
{
double u[n],v[n];
Randomize();
for (int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
nd_rnd(u);
nd_perpendicular(v,u);
mm_log->Lines->Add("U = "+nd_prn(u));
mm_log->Lines->Add("V = "+nd_prn(v));
mm_log->Lines->Add("(U.V) = "+AnsiString().sprintf("%6.3lf",nd_dot(u,v)));
}
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
并将此结果用于确认方法:
U = ( -0.526 -0.623 -0.535 -0.215 -0.044 )
V = ( 0.620 -0.023 -0.287 -0.682 -0.260 )
(U.V) = -0.000
U = ( 0.444 0.282 0.517 -0.203 0.644 )
V = ( 0.072 -0.564 -0.499 0.134 0.640 )
(U.V) = -0.000
U = ( 0.636 0.339 0.357 -0.022 -0.594 )
V = ( -0.559 -0.015 -0.108 -0.497 -0.655 )
(U.V) = 0.000
U = ( -0.626 -0.195 0.491 -0.374 -0.435 )
V = ( -0.722 -0.063 -0.541 0.039 0.424 )
(U.V) = 0.000
U = ( -0.532 -0.481 0.467 -0.517 0.019 )
V = ( 0.536 -0.716 -0.344 -0.205 -0.199 )
(U.V) = -0.000
U = ( 0.696 -0.588 0.018 -0.078 0.405 )
V = ( -0.106 -0.514 -0.645 -0.079 -0.550 )
(U.V) = 0.000
U = ( 0.072 0.679 0.124 -0.204 -0.690 )
V = ( 0.995 -0.058 0.041 0.060 0.037 )
(U.V) = -0.000
U = ( -0.742 -0.283 0.579 -0.150 0.109 )
V = ( -0.043 -0.798 -0.512 -0.308 -0.066 )
(U.V) = -0.000
U = ( 0.606 0.389 -0.551 0.041 -0.420 )
V = ( -0.457 -0.153 -0.489 -0.691 -0.228 )
(U.V) = 0.000
U = ( 0.947 -0.225 0.156 -0.075 0.151 )
V = ( 0.125 -0.153 -0.043 -0.034 -0.979 )
(U.V) = -0.000
[Edit1]随机性问题
正如@RoobieNuby指出的那样,上面的方法可能会有随机性问题(飞机不会有均匀分布)经过一些测试,我证实了这一点:
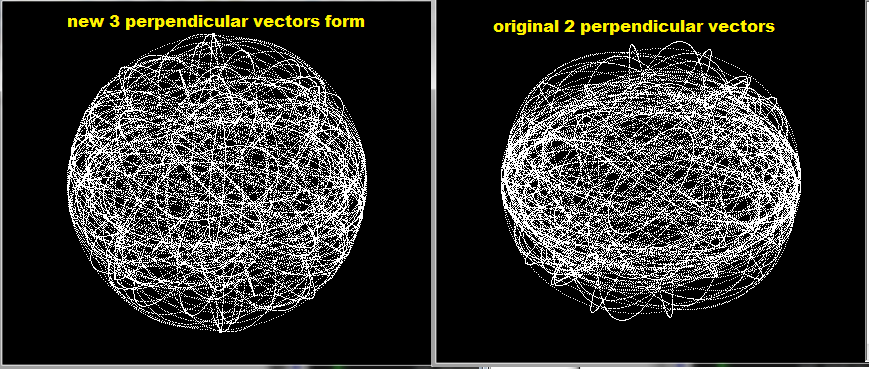
所以我测试了3和2基向量形式,可以直观地看到差异。右边是5D中的上述方法(截断为2D视图),左边是像这样获得的新形式:
//$$---- Form CPP ----
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <vcl.h>
#include <math.h>
#pragma hdrstop
#include "Unit1.h"
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#pragma package(smart_init)
#pragma resource "*.dfm"
TForm1 *Form1;
Graphics::TBitmap *bmp=NULL;
int xs=0,ys=0,**pyx=NULL;
const int n=5;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
double nd_dot(double *a,double *b) // = (a.b)
{
int i; double c;
for (c=0.0,i=0;i<n;i++) c+=a[i]*b[i];
return c;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void nd_unit(double *a) // a = a / |a|
{
int i; double c;
for (c=0.0,i=0;i<n;i++) c+=a[i]*a[i];
c=sqrt(c); if (c>1e-10) c=1.0/c; else c=0.0;
for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]*=c;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
double nd_length(double *a) // = |a|
{
int i; double c;
for (c=0.0,i=0;i<n;i++) c+=a[i]*a[i];
return sqrt(c);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void nd_rnd(double *a) // a = (? ? ? ... ?) , |a| = 1.0
{
int i; double c;
for (;;)
{
for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]=Random()-0.5;
for (c=0.0,i=0;i<n;i++) c+=a[i]*a[i];
if (c>1e-20) break;
}
c=1.0/sqrt(c);
for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]*=c;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void nd_perpendicular(double *a,double *b) // a = (? ? ? ... ?) , |a| = 1.0 , (a.b) = 0.0
{
if (n==1) // 1D case
{
if (fabs(b[0]>1e-10)) a[0]=1.0; else a[0]=1.0;
return;
}
int i; double c,s;
for (c=0.0,i=0;i<n;i++) // c = dot(a,b)
{
s=1.0; // s = signum of a[i] so (a.b) -> 0
if (b[i]<0.0) s=-1.0;
if (c*s>0.0) s=-s;
a[i]=s*Random();
c+=a[i]*b[i];
}
for (i=0;i<n;i++) // correct single element so (a.b) = 0
if (fabs(b[i])>1e-10)
{
c-=a[i]*b[i];
a[i]=-c/b[i];
break;
}
nd_unit(a);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void nd_perpendicular(double *a,double *b,double *c) // a = (? ? ? ... ?) , |a| = 1.0 , (a.b) = 0.0 , (a.c) = 0.0
{ // this is not in-place so (&a != &b) and (&a != &c)
int i,e; double ab,ac;
// spec cases
if (n<3) { for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]=0.0; return; }
// init
for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]=1.0;
ab = nd_dot(a,b);
ac = nd_dot(a,c);
// tune until dot products near zero
for (e=0;(e<1000)&&(fabs(ab)+fabs(ac)>=1e-5);e++) // max 1000 iterations so it will not hang up
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
ab-=a[i]*b[i];
ac-=a[i]*c[i];
if (fabs(b[i])>fabs(c[i])) a[i]=-ab/b[i];
else if (fabs(b[i])<fabs(c[i])) a[i]=-ac/c[i];
else if (fabs(ab)>=fabs(ac)) a[i]=-ab/b[i];
else a[i]=-ac/c[i];
ab+=a[i]*b[i];
ac+=a[i]*c[i];
}
nd_unit(a);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
AnsiString nd_prn(double *a)
{
int i; AnsiString s="( ";
for (i=0;i<n;i++) s+=AnsiString().sprintf("%6.3lf ",a[i]);
s+=" )"; return s;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// VCL application init (can ignore this)
__fastcall TForm1::TForm1(TComponent* Owner):TForm(Owner)
{
bmp=new Graphics::TBitmap;
bmp->HandleType=bmDIB;
bmp->PixelFormat=pf32bit;
if (bmp==NULL) Application->Terminate();
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------
// VCL application resize event (can ignore this)
void __fastcall TForm1::FormResize(TObject *Sender)
{
if (bmp==NULL) return;
xs=ClientWidth-mm_log->Width;
ys=ClientHeight;
bmp->SetSize(xs,ys);
xs=bmp->Width;
ys=bmp->Height;
if (pyx) delete[] pyx;
pyx=new int*[ys];
for (int y=0;y<ys;y++) pyx[y]=(int*)bmp->ScanLine[y];
Paint();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// VCL application exit (can ignore this)
void __fastcall TForm1::FormDestroy(TObject *Sender)
{
if (bmp) delete bmp; bmp=NULL;
if (pyx) delete[] pyx; pyx=NULL;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// VCL application repaint (consider this void main()...)
void __fastcall TForm1::FormPaint(TObject *Sender)
{
if (bmp==NULL) return;
if (pyx==NULL) return;
int i,e,x,y;
double u[n],v[n],w[n];
double a,da,x0,y0,r,c,s;
Randomize();
// clear screen (xs,ys is resolution, pyx is direct pixel access to bitmap bmp)
for (y=0;y<ys;y++)
for (x=0;x<xs;x++)
pyx[y][x]=0x00000000;
da=1.0*M_PI/180.0; // angle step
x0=0.5*xs; // center
y0=0.5*ys;
r=150.0; // radius
// 100 random circles
for (i=0;i<100;i++)
{
// 3 vector form
nd_rnd(w); // W random unit vector (normal of the plane)
nd_perpendicular(v,w); // V perpendicular to W
nd_perpendicular(u,v,w); // U perpendicular to V and W
// old 2 vector form
// nd_rnd(u);
// nd_perpendicular(v,u);
for (e=1,a=0.0;e;a+=da) // circle points loop
{
if (a>=2.0*M_PI) { e=0; a=0.0; }
c=r*cos(a);
s=r*sin(a);
x=double(x0+(c*u[0])+(s*v[0])); // use just x,y for render
y=double(y0+(c*u[1])+(s*v[1]));
if ((x>=0)&&(x<xs)&&(y>=0)&&(y<ys)) // if inside screen
pyx[y][x]=0x00FFFFFF; // render it
}
// debug info log to see the U,V,W as numbers
if (i==0)
{
mm_log->Text="";
mm_log->Lines->Add("U = "+nd_prn(u));
mm_log->Lines->Add("V = "+nd_prn(v));
mm_log->Lines->Add("W = "+nd_prn(w));
mm_log->Lines->Add("(U.V) = "+AnsiString().sprintf("%6.3lf",nd_dot(u,v)));
mm_log->Lines->Add("(U.W) = "+AnsiString().sprintf("%6.3lf",nd_dot(u,w)));
mm_log->Lines->Add("(W.V) = "+AnsiString().sprintf("%6.3lf",nd_dot(w,v)));
}
}
// refresh Application window with bitmap (bacbuffering)
Canvas->Draw(0,0,bmp);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// VCLo mouse wheel event ... just force repaint on mouse wheel to check the randomness in time (can ignore this)
void __fastcall TForm1::FormMouseWheel(TObject *Sender, TShiftState Shift, int WheelDelta, TPoint &MousePos, bool &Handled)
{
Paint();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
这里的重要内容是voidnd_perpendicular(double*a, double*b,double*c);函数,它将垂直向量返回给b,c。为了使N-D中的这种鲁棒性(在随机性很重要的情况下),您应该有n向量,而不仅仅是3。
函数的操作与上一个类似。区别只在于我们一次优化了不止一个点积。所以你需要选择每个轴优化哪个点积(基于垂直向量的abs坐标值)。所以你应该重写这个来一次优化n-1点积。
第一个向量(正常)第2个向量(1要优化的点积)第3个向量(2要优化的点积)第4个向量(3要优化的点积)第n个向量(n-1要优化的点积)2(除了第一个)向量作为基础(您可以随机选择它们)看起来只有3个向量就足够n
[Edit2]垂直于更多向量的向量…
从oher答案实现了点积垂直向量计算。以及垂直向量到多个向量的计算:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void nd_perpendicular(double *a,double *b) // a = (? ? ? ... ?) , |a| = 1.0 , (a.b) = 0.0
{
int i; double tmp[n],dot,len;
// |dot| limit to consider as non parallel
len=0.7*nd_length(b);
// tmp = random unit vector not parallel to b
for (;;)
{
nd_rnd(tmp);
dot=nd_dot(b,tmp);
if (fabs(dot)<=len) break;
}
// make a unit and perpendicular to b
for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]=tmp[i]-(dot*b[i]);
nd_unit(a);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void nd_perpendicular(double *a,double *v0,double *v1,double *v2=NULL,double *v3=NULL,double *v4=NULL,double *v5=NULL,double *v6=NULL,double *v7=NULL,double *v8=NULL,double *v9=NULL)
{
// this is not in-place so (&a != &b) and (&a != &c)
// a = unit vector perpendicular to all not NULL vectors v0,v1,v2,v3,...
const int M=10; // vi operands max count
int i,j,k,e,m; double dot[M],*v[M]={v0,v1,v2,v3,v4,v5,v6,v7,v8,v9},q;
// spec cases
if (n<3) { for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]=0.0; return; }
// init
for (i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]=1.0;
nd_rnd(a);
for (m=0,j=0;j<M;j++) if (v[j]) { m=j+1; dot[j]=nd_dot(a,v[j]); } else dot[j]=0.0;
// tune until dot products near zero
for (e=0;e<1000;e++) // max 1000 iterations so it will not hang up
{
for (q=0.0,j=0;j<m;j++) q+=fabs(dot[j]);
if (q<1e-3) { e=-1; break; }
// k = index of abs max dot
for (k=0,j=0;j<m;j++) if (fabs(dot[j])>=fabs(dot[k])) k=j;
// i = index of abs max coordinate of v[k]
for (i=0,j=0;j<n;j++) if (fabs(v[k][j])>=fabs(v[k][i])) i=j;
// update dots and a[i]
for (j=0;j<m;j++) dot[j]-=a[i]*v[j][i];
a[i]=-dot[k]/v[k][i];
for (j=0;j<m;j++) dot[j]+=a[i]*v[j][i];
}
if (e>=0)
for (e=0;e<1000;e++) // max 1000 iterations so it will not hang up
{
for (q=0.0,j=0;j<m;j++) q+=fabs(dot[j]);
if (q<1e-3) { e=-1; break; }
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
// k = index of abs max vec
for (k=0,j=0;j<m;j++) if (fabs(v[j][i])>=fabs(v[k][i])) k=j;
// update dots and a[i]
for (j=0;j<m;j++) dot[j]-=a[i]*v[j][i];
a[i]=-dot[k]/v[k][i];
for (j=0;j<m;j++) dot[j]+=a[i]*v[j][i];
}
}
nd_unit(a);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
太增强鲁棒性它使用2种不同的迭代方法。这里的用法示例(n=5):
// nd_perpendicular test
double V[n][n]; int x,y;
nd_rnd(V[0]);
nd_perpendicular(V[1],V[0]);
nd_perpendicular(V[2],V[1],V[0]);
nd_perpendicular(V[3],V[2],V[1],V[0]);
nd_perpendicular(V[4],V[3],V[2],V[1],V[0]);
for (x=0;x<n;x++)
for (y=x+1;y<n;y++)
mm_log->Lines->Add(AnsiString().sprintf("(V%i.V%i) = %6.3lf",x,y,nd_dot(V[x],V[y])));
下面假设高维圆是指一个N球体与包含球体中心的N超平面(即N 1空间中的N球体)的交集。
您可以执行以下操作(假设您在N 1空间中,考虑到N个球体):