

我正在寻找一种算法,可以在小分辨率下绘制一个漂亮3D球体。我找到了Bresenham的圆算法,但它是用于2D绘图的。我只需要球体边界(我不需要它填充)。我也谷歌了这个问题的解决方案,但我什么也没找到。这篇文章没有帮助(什么是蛮力算法?)。我不能使用任何OpenGL库,我需要vanilla C/C解决方案。提前谢谢你。
如果我做对了,你想渲染球体的所有表面体素
蛮力是O(R^3)。如果你只是从平面投射光线并计算第3个坐标,那么你会得到O(R^2),但是为了确保没有Voxels丢失,你必须从仍然是O(R^2)的所有3个平面进行投影
它看起来像这样:
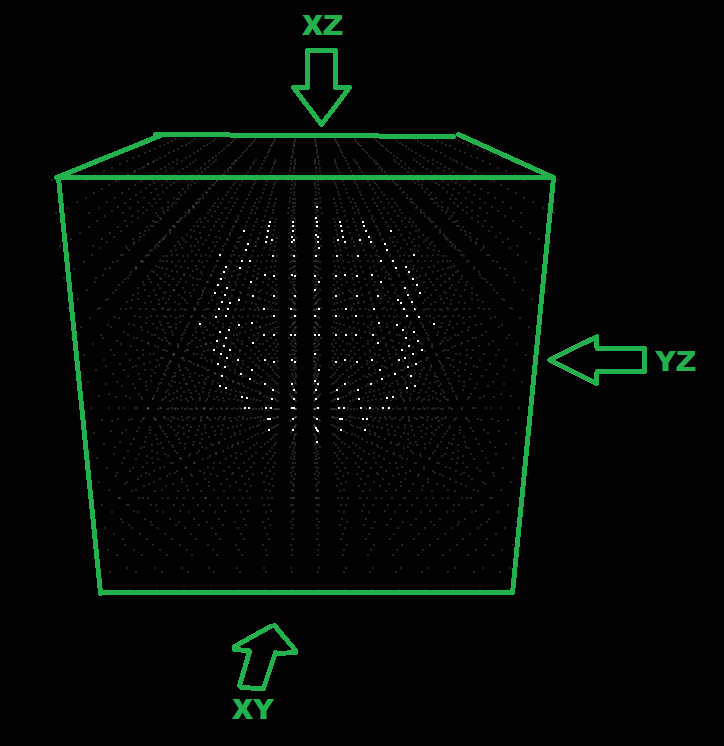
LED多维数据集16x16x16模拟。现在算法:
>
计算可见边界框
不需要渲染整个渲染空间,只是球体的中心 /-半径…
以一架飞机(XY为例)
从边界框内的所有x, y点投射光线,该框仅为2 for循环,并通过球体方程计算光线击中的z坐标:
(x-x0)^2 + (y-y0)^2 + (z-z0)^2 = R^2
所以
z=z0 +/- sqrt(R^2 - (x-x0)^2 - (y-y0)^2)
并渲染两个体素。int sqrt(int x)用于有限大小(如LED立方体/屏幕或体素空间)可以通过LUT查找表来完成,以加快速度。
对所有平面执行步骤#2(xy, yz,xz)
C中的代码如下所示:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
//--- LED cube class ver: 1.00 ----------------------------------------------
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#ifndef _LED_cube_h
#define _LED_cube_h
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
const int _LED_cube_size=16;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
class LED_cube
{
public:
int n,map[_LED_cube_size][_LED_cube_size][_LED_cube_size];
LED_cube() { n=_LED_cube_size; }
LED_cube(LED_cube& a) { *this=a; }
~LED_cube() { }
LED_cube* operator = (const LED_cube *a) { *this=*a; return this; }
//LED_cube* operator = (const LED_cube &a) { /*...copy...*/ return this; }
void cls(int col); // clear cube with col 0x00BBGGRR
void sphere(int x0,int y0,int z0,int r,int col); // draws sphere surface with col 0x00BBGGRR
void glDraw(); // render cube by OpenGL as 1x1x1 cube at 0,0,0
};
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LED_cube::cls(int col)
{
int x,y,z;
for (x=0;x<n;x++)
for (y=0;y<n;y++)
for (z=0;z<n;z++)
map[x][y][z]=col;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LED_cube::sphere(int x0,int y0,int z0,int r,int col)
{
int x,y,z,xa,ya,za,xb,yb,zb,xr,yr,zr,xx,yy,zz,rr=r*r;
// bounding box
xa=x0-r; if (xa<0) xa=0; xb=x0+r; if (xb>n) xb=n;
ya=y0-r; if (ya<0) ya=0; yb=y0+r; if (yb>n) yb=n;
za=z0-r; if (za<0) za=0; zb=z0+r; if (zb>n) zb=n;
// project xy plane
for (x=xa,xr=x-x0,xx=xr*xr;x<xb;x++,xr++,xx=xr*xr)
for (y=ya,yr=y-y0,yy=yr*yr;y<yb;y++,yr++,yy=yr*yr)
{
zz=rr-xx-yy; if (zz<0) continue; zr=sqrt(zz);
z=z0-zr; if ((z>0)&&(z<n)) map[x][y][z]=col;
z=z0+zr; if ((z>0)&&(z<n)) map[x][y][z]=col;
}
// project xz plane
for (x=xa,xr=x-x0,xx=xr*xr;x<xb;x++,xr++,xx=xr*xr)
for (z=za,zr=z-z0,zz=zr*zr;z<zb;z++,zr++,zz=zr*zr)
{
yy=rr-xx-zz; if (yy<0) continue; yr=sqrt(yy);
y=y0-yr; if ((y>0)&&(y<n)) map[x][y][z]=col;
y=y0+yr; if ((y>0)&&(y<n)) map[x][y][z]=col;
}
// project yz plane
for (y=ya,yr=y-y0,yy=yr*yr;y<yb;y++,yr++,yy=yr*yr)
for (z=za,zr=z-z0,zz=zr*zr;z<zb;z++,zr++,zz=zr*zr)
{
xx=rr-zz-yy; if (xx<0) continue; xr=sqrt(xx);
x=x0-xr; if ((x>0)&&(x<n)) map[x][y][z]=col;
x=x0+xr; if ((x>0)&&(x<n)) map[x][y][z]=col;
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void LED_cube::glDraw()
{
#ifdef __gl_h_
int x,y,z;
float p[3],dp=1.0/float(n-1);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBlendFunc(GL_ONE,GL_ONE);
glPointSize(2.0);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
for (p[0]=-0.5,x=0;x<n;x++,p[0]+=dp)
for (p[1]=-0.5,y=0;y<n;y++,p[1]+=dp)
for (p[2]=-0.5,z=0;z<n;z++,p[2]+=dp)
{
glColor4ubv((BYTE*)(&map[x][y][z]));
glVertex3fv(p);
}
glEnd();
glDisable(GL_BLEND);
glPointSize(1.0);
#endif
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#endif
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
类使用:
LED_cube cube;
cube.cls(0x00202020); // clear space to dark gray color
int a=cube.n>>1; // just place sphere to middle and size almost the whole space
int r=a-3;
cube.sphere(a,a,a,r,0x00FFFFFF);
cube.glDraw(); // just for mine visualization you have to rewrite it to your rendering system
如果您只想使用C,请将类分解为全局函数和变量,并将C运算符x,--,=,-=,*=,…转换为C样式x=x 1,…
根据链接,看起来你对球体的体素算法更感兴趣,而不是图形本身;说一些像这页帮助的东西。你不想要一个球,但只想要表面。
中点圆算法可用于绘制3D体素球体:将球体视为一堆切片,每个切片包含一个圆。
在实践中,你使用两个嵌套的中点圆,外部定义内部的半径。(虽然在彼此之上绘制圆圈的朴素算法可能会在体素上留下洞,但中点圆算法利用了对称性,如果正确实现,就不会出现这样的洞。)
你一前一后建造六个盖子,就像把一个立方体雕刻成一个球体一样。由于每个盖子的表面斜率总是小于1,所以在盖子上向外移动最多会使每个坐标改变1,所以不会出现孔。
这种方法的问题在于复杂性:你计算的每个点可能会影响多达48个体素细胞。(在每个上限中,每个点都在一个八进制中计算,因此会影响8个细胞。有6个上限,6*8=48。)
我建议采取不同的方法。
以x0,y0,z0为中心的半径球面的方程是
(x-x0)2(y-y0)2(z-z0)2=r2
使用整数坐标,网格点很少精确地在球体表面上,允许一系列值:
RRMIN≤(x-x0)2(y0)2(z-z0)2≤RRMAX
其中RRMIN和RRMAX是常数;具体来说,到球心的最小和最大距离的平方。
我建议在一般情况下使用双坐标。这允许您选择球体的中心是以坐标为中心(暗示奇数直径),还是以两个相邻的心形线为中心(暗示偶数直径)。
如果您有一个SIZE×SIZE×SIZE体素网格(灯光、积木等),那么
int sphere_surface(const char x, const char y, const char z,
const char size, const int rrmin, const int rrmax)
{
const int center = size - (size & 1); /* Size rounded down to even integer */
const int dx = center - x - x,
dy = center - y - y,
dz = center - z - z; /* Doubled coordinates */
const int rr = dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz; /* Distance squared */
return (rrmin <= rr) && (rr <= rrmax);
}
如果点(x,y,z)位于立方体中心的球体表面区域内,则返回1。(从技术上讲,如果从该点到size大小的立方体的中心的距离在sqrt(rrmin)/2和sqrt(rrmax)/2范围内,则返回。)
rrmin和rrmax的“正确”值高度依赖于上下文。rrmax通常接近size*size(请记住,该函数使用加倍坐标),rrmin稍微少一点。
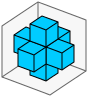
例如,如果您有一个3×3×3的网格,您只希望每个面上的六个中心单元格满足条件;您可以使用size=3、rrmin=1、rrmax=4来做到这一点:
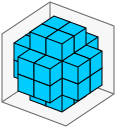
如果你有一个4×4×4的网格,你希望每个面上的四个中心单元格满足条件(所以64个单元格中总共有24个被认为是在球面上);你可以使用size=4,rrmin=11,rrmax=11来做到这一点:
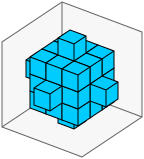
通过5×5×5网格,我们得到了上述算法的有趣副作用。
size=5,rrmin=8,rrmax=16产生一个非常“有角”的球体,几乎是一个站在角落里的立方体:
size=5,rrmin=12,rrmax=20产生我最喜欢的近似球体:
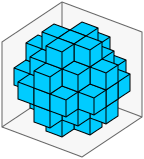
size=5,rrmin=16,rrmax=24产生一个圆形立方体(每个面为3×3平面):
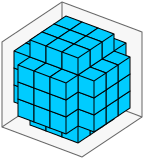
显然,使用rrmin=0也包括所有内部单元,产生一个球而不仅仅是球体的表面。
随着网格大小的增加,您可以表示的每个大小球体的变体越多。
上述功能在微控制器上特别有用,因为您可以简单地遍历点阵,根据需要更新每个点的状态。此外,大多数微控制器内存紧张,但具有非常快的(单时钟)加法、减法和乘法指令。(尽管具有32位结果的16×16位乘法通常需要两个或更多指令。)
典型的微控制器没有ROM/闪存功能来存储足够有趣的体素模式,只有少数具有通过SPI从SD卡DMA的功能(因此您可以从microSD卡加载体素模式的“帧”),但是像上面这样的功能可以用很少的输入产生有趣的形状-特别是您可以插值的输入。
上述函数也可以适用于近似反化(通过将rr与rrmin和rrmax进行比较),以防您的体素不仅仅是二进制的,而是例如PWM控制的LED。
由于可视化上面的内容通常有点困难,下面是我用来生成上面图像的快速小技巧。当给定size、rrmin和rrmax作为命令行参数时,它将SVG图像输出到标准输出,将ASCII切片输出到标准错误。
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define BORDER 2
#define XC(x,y,z) ((x)*16 + (y)*12)
#define YC(x,y,z) ((x)*6 - (y)*8 - (z)*17)
static int xt = 0;
static int yt = 0;
static void fcube(FILE *out, const int x, const int y, const int z, const int fill)
{
const int xc = xt + XC(x,y,z);
const int yc = yt + YC(x,y,z);
fprintf(out, "<path d=\"M%d,%dl16,6,12,-8,0,-17,-16,-6,-12,8z\" fill=\"#%06x\" stroke=\"#000\" />\n", xc, yc, fill & 0xFFFFFF);
fprintf(out, "<path d=\"M%d,%dl16,6,12,-8m-12,8l0,17\" fill=\"none\" stroke=\"#000\" />\n", xc, yc-17);
}
static unsigned long rrmin = 0UL;
static unsigned long rrmax = 0UL;
static int center = 0;
static int surface(const int x, const int y, const int z)
{
/* Doubled coordinates: */
const long dx = 2*x - center,
dy = 2*y - center,
dz = 2*z - center;
const unsigned long rr = dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz;
return (rrmin <= rr) && (rr <= rrmax);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int width, height;
int size, x, y, z;
char dummy;
if (argc != 4 || !strcmp(argv[1], "-h") || !strcmp(argv[1], "--help")) {
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s SIZE RRMIN RRMAX\n", argv[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "Where\n");
fprintf(stderr, " SIZE is the size of the voxel cube\n");
fprintf(stderr, " RRMIN is the minimum distance squared, and\n");
fprintf(stderr, " RRMAX is the maximum distance squared,\n");
fprintf(stderr, " using doubled coordinates.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Examples:\n");
fprintf(stderr, " %s 3 1 4\n", argv[0]);
fprintf(stderr, " %s 4 11 11\n", argv[0]);
fprintf(stderr, " %s 5 8 16\n", argv[0]);
fprintf(stderr, " %s 5 12 20\n", argv[0]);
fprintf(stderr, " %s 5 16 24\n", argv[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (sscanf(argv[1], " %d %c", &size, &dummy) != 1 || size < 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: Invalid size.\n", argv[1]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (sscanf(argv[2], " %lu %c", &rrmin, &dummy) != 1) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: Invalid rrmin.\n", argv[2]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (sscanf(argv[3], " %lu %c", &rrmax, &dummy) != 1 || rrmax < rrmin) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: Invalid rrmax.\n", argv[3]);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
/* Calculate coordinate range. */
{ int xmin = XC(0,0,0);
int ymin = YC(0,0,0);
int xmax = XC(0,0,0);
int ymax = YC(0,0,0);
for (z = 0; z <= size; z++)
for (y = 0; y <= size; y++)
for (x = 0; x <= size; x++) {
const int xc = XC(x,y,z);
const int yc = YC(x,y,z);
if (xc < xmin) xmin = xc;
if (xc > xmax) xmax = xc;
if (yc < ymin) ymin = yc;
if (yc > ymax) ymax = yc;
}
xt = BORDER - xmin;
width = xmax - xmin + 2*BORDER;
yt = BORDER - ymin;
height = ymax - ymin + 2*BORDER;
}
center = size - 1;
/* SVG preamble. */
printf("<?xml version=\"1.0\"?>\n");
printf("<svg xmlns=\"http://www.w3.org/2000/svg\" viewBox=\"0 0 %d %d\">\n", width, height);
printf("<path d=\"M%d,%dL%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%dz\" fill=\"#f7f7f7\" stroke=\"#666666\"/>\n",
xt+XC( 0, 0, 0), yt+YC( 0, 0, 0),
xt+XC(size, 0, 0), yt+YC(size, 0, 0),
xt+XC(size,size, 0), yt+YC(size,size, 0),
xt+XC(size,size,size), yt+YC(size,size,size),
xt+XC(0, size,size), yt+YC( 0,size,size),
xt+XC(0, 0,size), yt+YC( 0, 0,size));
printf("<path d=\"M%d,%dL%d,%d,%d,%dM%d,%dL%d,%d\" fill=\"none\" stroke=\"#666666\"/>\n",
xt+XC( 0, 0, 0), yt+YC( 0, 0, 0),
xt+XC( 0,size, 0), yt+YC( 0,size, 0),
xt+XC(size,size, 0), yt+YC(size,size, 0),
xt+XC( 0,size, 0), yt+YC( 0,size, 0),
xt+XC( 0,size,size), yt+YC( 0,size,size));
for (z = 0; z < size; z++)
for (y = size - 1; y >= 0; y--)
for (x = 0; x < size; x++)
if (surface(x,y,z))
fcube(stdout, x, y, z, 0x00CCFF);
printf("</svg>\n");
for (z=0; z < size; z++) {
for (y = 0; y < size; y++) {
for (x = 0; x < size; x++)
fputc(surface(x,y,z) ? 'X' : '.', stderr);
fputs(" ", stderr);
for (x = 0; x < size; x++)
fputc(surface(x,z,y) ? 'X' : '.', stderr);
fputs(" ", stderr);
for (x = 0; x < size; x++)
fputc(surface(y,z,x) ? 'X' : '.', stderr);
fputc('\n', stderr);
}
fputc('\n', stderr);
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
我没有费心去处理输出;你可以很容易地为每个脸选择不同的颜色,也许在背景平面上添加阴影,等等。
上面的图像是使用这个程序创建的,然后使用GIMP转换为PNG,但我建议使用浏览器在本地查看生成的文件。
问题?
在这个领域中使用的最常见的库是openGL,这张幻灯片向您展示了如何在IDE上配置库从这里下载文件http://www.xmission.com/~nate/glut.html然后将它们放在这个路径中。
opengl-超级圣经-第4本这是一本从零开始到高级水平的教科书