从循环链表末尾删除节点的Java程序
1 简介
在此程序中,我们将创建一个循环链表,并从列表末尾删除一个节点。如果列表为空,将显示消息“列表为空”。如果列表不为空,我们将循环链表,直到到达倒数第二个节点。我们将倒数第二个节点作为新的尾巴,而这个新的尾巴将指向头并删除前一个尾巴。
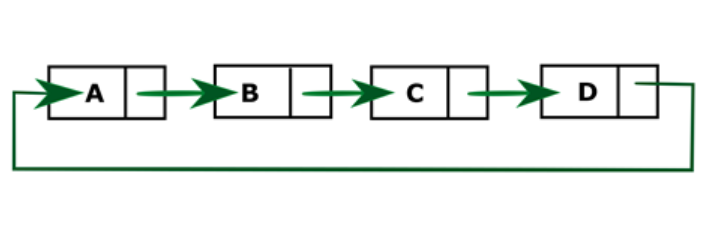
从末端删除节点后的循环链表
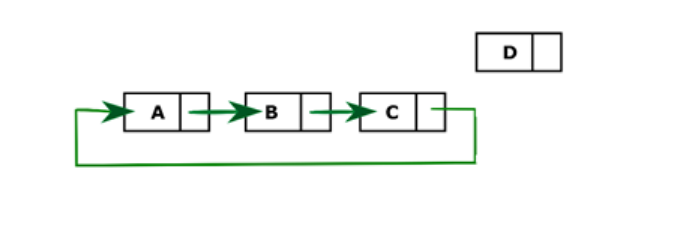
在上面的链表中,D是最后一个需要删除的节点。我们将遍历列表直到C。将C设为新尾巴,C指向头A。
2 算法思路
- 定义一个Node类,该类代表列表中的一个节点。它具有两个属性数据,下一个将指向下一个节点。
- 定义另一个用于创建循环链表的类,它具有两个节点:head和tail。它有两种方法:deleteEnd()和display()。
- deleteEnd()将从列表末尾删除该节点:
- 它首先检查head是否为空(空列表),然后它将从函数返回,因为列表中没有节点。
- 如果列表不为空,它将检查列表是否只有一个节点。
- 如果列表中只有一个节点,则它将head和tail都设置为null。
- 如果列表中有多个节点,则循环遍历直到current.next!= tail。
- 现在,临时节点将指向尾部之前的节点。使临时节点为新的尾巴,然后尾巴将指向头部,从最后删除该节点。
- 定义一个新节点“current”,该节点将指向头部。
- 打印current.data,直到current再次指向head。
- 当前将在每次迭代中指向列表中的下一个节点。
3 程序实现
/**
* 一点教程网: http://www.yiidian.com
*/
public class DeleteEnd {
//Represents the node of list.
public class Node{
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
//Declaring head and tail pointer as null.
public Node head = null;
public Node tail = null;
//This function will add the new node at the end of the list.
public void add(int data){
//Create new node
Node newNode = new Node(data);
//Checks if the list is empty.
if(head == null) {
//If list is empty, both head and tail would point to new node.
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
}
else {
//tail will point to new node.
tail.next = newNode;
//New node will become new tail.
tail = newNode;
//Since, it is circular linked list tail will point to head.
tail.next = head;
}
}
//Deletes node from end of the list
public void deleteEnd() {
//Checks whether list is empty
if(head == null) {
return;
}
else {
//Checks whether contain only one element
if(head != tail ) {
Node current = head;
//Loop will iterate till the second last element as current.next is pointing to tail
while(current.next != tail) {
current = current.next;
}
//Second last element will be new tail
tail = current;
//Tail will point to head as it is a circular linked list
tail.next = head;
}
//If the list contains only one element
//Then it will remove it and both head and tail will point to null
else {
head = tail = null;
}
}
}
//Displays all the nodes in the list
public void display() {
Node current = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
}
else {
do{
//Prints each node by incrementing pointer.
System.out.print(" "+ current.data);
current = current.next;
}while(current != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DeleteEnd cl = new DeleteEnd();
//Adds data to the list
cl.add(1);
cl.add(2);
cl.add(3);
cl.add(4);
//Printing original list
System.out.println("Original List: ");
cl.display();
while(cl.head != null) {
cl.deleteEnd();
//Printing updated list
System.out.println("Updated List: ");
cl.display();
}
}
}
输出结果为:
Original List:
1 2 3 4
Updated List:
1 2 3
Updated List:
1 2
Updated List:
1
Updated List:
List is empty
热门文章
优秀文章


