Java Guava Longs类
1 什么是Guava Longs类
Longs 是原始类型 long 的实用程序类。
2 Guava Longs类的语法
@GwtCompatible
public final class Longs
extends Object
3 Guava Longs类的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| static List<Long> asList(long... backingArray) | 返回由指定数组支持的固定大小列表,类似于 Arrays.asList(Object[])。 |
| static int compare(long a, long b) | 比较两个指定的 long 值。 |
| static long[] concat(long[]... arrays) | 返回每个提供的数组中组合成单个数组的值。 |
| static boolean contains(long[] array, long target) | 如果目标作为数组中任何位置的元素存在,则返回 true。 |
| static long[] ensureCapacity(long[] array, int minLength, int padding) | 返回包含与数组相同的值的数组,但保证具有指定的最小长度。 |
| static long fromByteArray(byte[] bytes) | 返回 long 值,其 big-endian 表示存储在字节的前 8 个字节中;相当于 ByteBuffer.wrap(bytes).getLong()。 |
| static long fromBytes(byte b1, byte b2, byte b3, byte b4, byte b5, byte b6, byte b7, byte b8) | 以 big-endian 顺序返回字节表示为给定 8 个字节的 long 值;相当于 Longs.fromByteArray(new byte[] {b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, b6, b7, b8})。 |
| static int hashCode(long value) | 返回值的哈希码;等于调用 ((Long) value).hashCode() 的结果。 |
| static int indexOf(long[] array, long target) | 返回值目标在数组中第一次出现的索引。 |
| static int indexOf(long[] array, long[] target) | 返回指定目标在数组中第一次出现的起始位置,如果没有这样的出现,则返回 -1。 |
| static String join(String separator, long... array) | 返回一个字符串,其中包含由分隔符分隔的提供的long值。 |
| static int lastIndexOf(long[] array, long target) | 返回值目标在数组中最后一次出现的索引。 |
| static Comparator<long[]> lexicographicalComparator() | 返回按字典顺序比较两个long数组的比较器。 |
| static long max(long... array) | 返回数组中存在的最大值。 |
| static long min(long... array) | 返回数组中存在的最小值。 |
| static Converter<String,Long> stringConverter() | 返回一个可序列化的转换器对象,该对象使用 Long.decode(java.lang.String) 和 Long.toString() 在字符串和长整数之间进行转换。 |
| static long[] toArray(Collection<? extends Number> collection) | 返回一个包含collection的每个值的数组,以Number.longValue()的方式转换为long值。 |
| static byte[] toByteArray(long value) | 返回 8 元素字节数组中值的big-endian表示;相当于 ByteBuffer.allocate(8).putLong(value).array()。 |
| static Long tryParse(String string) | 将指定的字符串解析为带符号的十进制long值。 |
5 Guava Longs类的例子
让我们看一个简单的Guava Longs类示例。
package com.yiidian;
import com.google.common.primitives.Longs;
import java.util.List;
public class GuavaTester {
public static void main(String args[]) {
GuavaTester tester = new GuavaTester();
tester.testLongs();
}
private void testLongs() {
long[] longArray = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
//convert array of primitives to array of objects
List<Long> objectArray = Longs.asList(longArray);
System.out.println(objectArray.toString());
//convert array of objects to array of primitives
longArray = Longs.toArray(objectArray);
System.out.print("[ ");
for(int i = 0; i< longArray.length ; i++) {
System.out.print(longArray[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("]");
//check if element is present in the list of primitives or not
System.out.println("5 is in list? "+ Longs.contains(longArray, 5));
//Returns the minimum
System.out.println("Min: " + Longs.min(longArray));
//Returns the maximum
System.out.println("Max: " + Longs.max(longArray));
//get the byte array from an integer
byte[] byteArray = Longs.toByteArray(20000);
for(int i = 0; i< byteArray.length ; i++) {
System.out.print(byteArray[i] + " ");
}
}
}
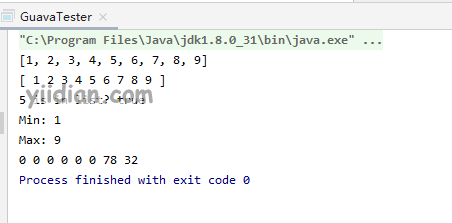
输出结果为:
热门文章
优秀文章


